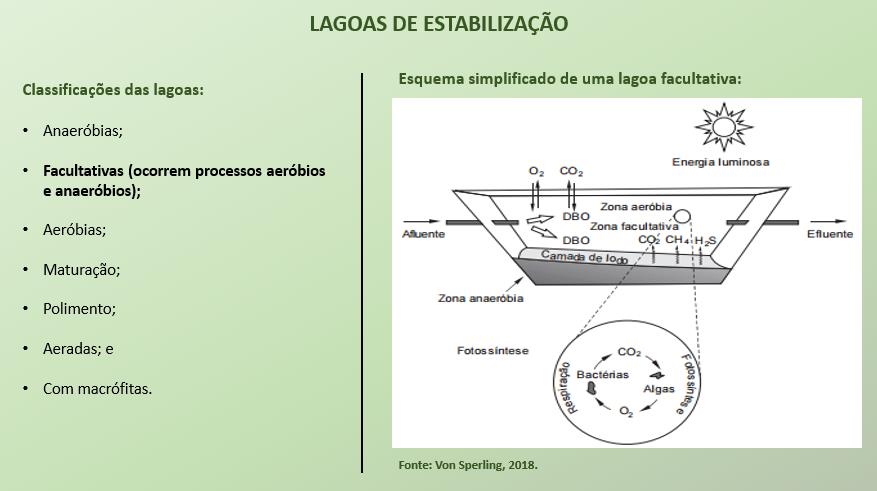
Stabilization ponds are biological treatment systems in which the stabilization of organic matter is carried out by bacteriological oxidation (aerobic oxidation or anaerobic fermentation) and / or photosynthetic reduction of algae.
In general, ponds have excellent treatment efficiencies. In terms of BOD removal efficiency, the typical range is between 75 and 85%. With regard to coliform removal, up to 99.9% efficiency has been achieved.
Pond efficiencies are influenced, in large part, by climate. Locations with predominant warm climate (eg, Brazil) have higher removal efficiencies than cold locations, because temperature has a relationship with other factors that interfere with the biological process, such as solar radiation, photosynthesis velocity and metabolism of organisms.
In addition, it is important to highlight the role of algae in facultative and aerobic lagoons. In these two types of systems, algae are responsible for the delivery of much of the oxygen dissolved in the pond, which will be used by microorganisms to synthesize organic matter.
CLASSIFICATION OF LAGOONS:
The lagoons are classified into: anaerobic; (aerobic and anaerobic processes occur); aerobic; maturation; polishing; aerated; and macrophytes.
BENEFITS:
The main advantages are: high efficiency of removal of BOD and coliforms; reduced operation and maintenance costs; and simplicity of operation.
DISADVANTAGES:
The main disadvantages are: they require large areas; biological activity affected by temperature; and generation of bad odors (anaerobic processes).